The GDPR is a legislation that sets a new standard on how personal data is collected, protected, and processed, with emphasis on privacy rights and transparency.
So, if you’re wondering what is the purpose of GDPR, simply put, companies need to report serious data breaches per these regulations.
In the event a breach occurs, both affected individuals and the relevant supervisory authority need to be notified within 72 hours of its discovery.
What is GDPR?
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a key legislation designed to specifically modernize how data privacy is governed across the European Union. It was approved by the European Parliament on April 14, 2016 and it officially came into effect on May 25 in 2018.
What is the Purpose of the GDPR?
The purpose of GDPR is to safeguard individuals and their personal data by having companies handle this information with great care and responsibility. It sets clear standards for data security, protection of personal data against unlawful and unauthorized processing, and events like destruction, damage or accidental loss.
When looking for answers on what is the main purpose of the GPDR, you need to look at what this policy defines.
That said, the GDPR clearly outlines why personal data is collected with emphasis put on its use and purpose. This regulation also enforces data minimization, meaning only the vital and necessary data for a specific purpose can be collected.
Moreover, companies are fully responsible for keeping the data accurate and up to date.
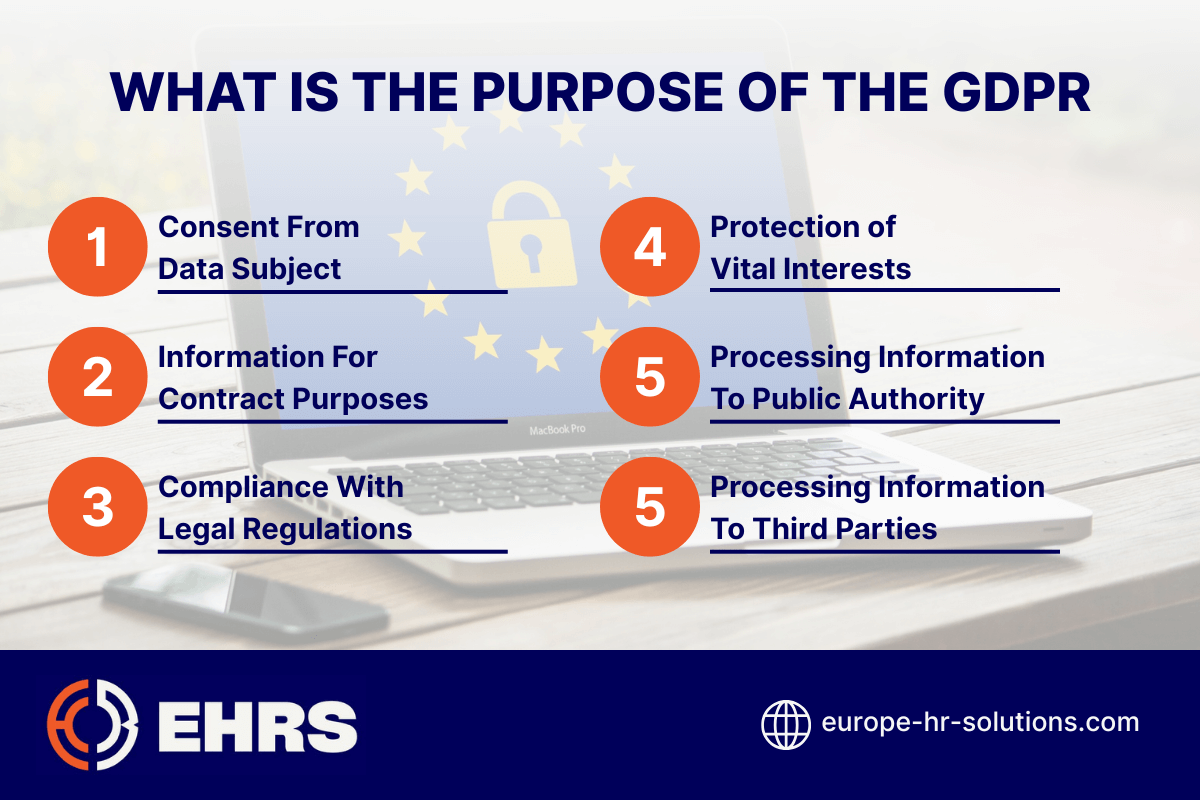
According to these guidelines, companies are not authorized to process personally identifiable information (PII) if they do not meet the following six lawful bases for processing:
- Consent – companies need consent from the subject
- Contract – processing information with subject for contract purposes
- Regulations – processing of any information needs to comply with legal obligations
- Interests – processing of any information needs to protect the vital interests of the subject
- Performance – processing information that is required for a task in the interest of the public or official authority
- Legal – processing of any information that is required by a third party unless it is overridden by the subject’s freedoms and rights
History of GDPR
To understand what is the purpose of GDPR, and why it is important, we need to go back in time a bit. The first origins of the GDPR originate in 1950 during the European Convention on Human Rights when fundamental rights were established that member states are obligated to uphold.
With computers entering the fray in the later years, there was a need for further regulations. Companies, businesses, and the government saw a widespread use of computers, and in 1981, the Data Protection Convention recognized privacy as a legal right.
That said, the 1995 European Data Protection Directive was a direct predecessor to the GDPR and laid the groundwork for what is today’s most comprehensive data protection framework.
GDPR Principles, Scope & Penalties
The GDPR is founded on seven core principles and these guide its compliance requirements and regulations regarding personal data:
- Lawfulness, fairness, and transparency – data subjects must be clearly informed about how their data will be used
- Purpose limitation – data can only be collected for specific, legitimate purposes
- Data minimization – the amount of data collected should be limited to what is necessary for the intended processing
- Accuracy – companies must ensure data is accurate and kept up to date. Data should be corrected or deleted upon the subject’s request
- Storage limitation – personal data must not be retained longer than necessary
- Integrity and confidentiality – adequate security measures must protect personal data from theft or unauthorized access
- Accountability – companies are responsible for demonstrating and ensuring compliance with the GDPR
These foundation principles also include various data subject rights, such as the following:
- Right to be forgotten – individuals can request that their personal data be erased from a company’s records. Companies may refuse such requests only if they have a valid legal reason
- Right of access – data subjects have the right to review the personal data a company holds about them
- Right to object – individuals can oppose the processing or use of their personal data. Companies must respect this unless they can justify the processing under one of the GDPR’s lawful bases – and they must inform the subject of their decision and reasoning
- Right to rectification – subjects can request corrections to any inaccurate personal information
- Right of portability – individuals can obtain and transfer their personal data from one organization to another
What is the Purpose of GDPR in AI
The GDPR instructs that only the minimum necessary data can be used for any specific purpose. This means that AI systems need to comply with this principle and avoid the collection and/or manipulation of unnecessary data.
What’s more, data that is collected for one purpose cannot be used and/or repurposed without acquiring prior additional consent from the subject.
What is the Purpose of GDPR Compliance
Every company that collects personal data from citizens within an EU member state needs to comply with GDPR, even if that company is based outside the EU. Compliance is obligatory whenever personal data of a European citizen is collected, regardless of where the company is located.
After all, what is the purpose of GDPR if the data is not handled the right way?
The GDPR applies to all methods of collecting data. This means online or internet based tools, as well as physical ways of collecting. It defines the three key roles to personal data:
- Data subject – the individual who owns the personal data
- Data controller – the person or company that determines what personal data is collected and how it will be used
- Data processor – the person or company that processes personal data on behalf of the data controller
How to Ensure Compliance
Knowing what is the purpose of GDPR is one thing, but knowing how to ensure compliance is a whole different ball game.
While the GDPR outlines the responsibility in data management, it does not mandate which specific technical measures companies need to implement.
With that in mind, here are the best practices to ensure compliance:
- Always acquire explicit consent before collecting personal data
- Collect only data that is necessary as companies remain responsible for all data tehy gather
- Do not share personal data with third parties unless users have given their consent and there is supervisory authority present
- Encrypt personal data and maintain at least two secure copies at separate locations
- Use tools that would allow for easy editing and/or deleting of personal data with the ability to document and verify these actions
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What are the Means and Purposes of the GDPR?
The GDPR requires personal data to be processed exclusively for legitimate purposes with prior consent from the subject at the time of collection.
Additionally, companies need to collect and process only the minimum amount of data necessary for these purposes.
What are the Key Objectives of GDPR?
The key objectives of GDPR is to ensure that public administrations adhere to the key principles set in place, including lawful processing, fair processing, purpose limitation, strict data retention, and data minimization policies.
What is the Principle of Purpose in GDPR?
Purpose limitation means that personal data needs to be collected only for explicit, legitimate, and specified purposes and must not be processed any further.
What is the Need for GDPR?
The GDPR safeguards people’s privacy by making sure their personal information is well protected. This regulation applies to all companies and they need to ensure compliance or face significant fines and penalties for non-compliance.